National Institute of Standards and Technology
Derived Test Requirements
for FIPS PUB 140-1,
Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules
PART 3
(Sections 8-11)
March 1995
Final
8. CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEY MANAGEMENT
General
AS08.01: Documentation shall specify all aspects
of key management for the cryptographic module. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.01.01: The vendor documentation shall
describe key management for the module. At a minimum, the documentation
shall specify the following information:
-
Key material, such as:
-
List all types of keys used by the module, both internally and externally
generated
-
Explain function of each key
-
Specify format of all entered and output keys
-
Discuss how all keys are protected
-
Key generation, such as:
-
Describe the key-generation process
-
Specify whether the key generation algorithm is FIPS-approved
-
Specify which types of keys are generated
-
Key distribution, such as:
-
Describe key distribution technique
-
Indicate whether technique is FIPS-approved
-
Indicate which types of keys must be distributed
-
Key entry and output, such as:
-
Describe key entry procedures
-
Describe key output procedures
-
Indicate whether manual or electronic key entry is used
-
Indicate whether manual or electronic key output is used
-
Indicate which types of keys are manually entered or output
-
Indicate which types of keys are electronically entered or output
-
Indicate form in which keys are entered or output (plaintext, encrypted
form, under split knowledge procedures)
-
Indicate use of a manual key entry test for verification of entered keys
-
Key storage, such as:
-
Indicate which types of keys are stored
-
Indicate where they are stored
-
Indicate the form in which they are stored (plaintext, encrypted form,
under split knowledge procedures)
-
Key destruction, such as:
-
Describe key destruction technique and mechanisms
-
Indicate any restrictions on when the module can be zeroized
-
Indicate which types of keys are zeroized and why
-
Indicate which security parameters are zeroized and why
-
Indicate which types of keys and security parameters are not zeroized and
why
-
Key archiving, such as:
-
Whether key archiving is used
-
Describe key archiving technique
-
Indicate which types of keys can be archived
-
Indicate whether keys are encrypted for archiving
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.01.01: The tester shall review the vendor
documentation to verify that, at a minimum, the information specified in
VE08.01.01 is included.
-
TE08.01.02: The tester shall perform tests
in these categories as specified by AS08.04-AS08.20.
AS08.02: Secret keys and private keys shall
be protected from unauthorized disclosure, modification and substitution.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.02.01: The vendor documentation shall
describe the protection of all secret and/or private keys internal to the
module as required by item 1 under VE08.01.01. Protection shall include
the implementation of mechanisms that protect against unauthorized disclosure,
unauthorized modification, and unauthorized substitution.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.02.01: The tester shall check the vendor
documentation that describes the protection of secret and/or private keys.
The tester shall verify that the documentation describes how thesekeys
will be protected from unauthorized disclosure, unauthorized modification,
and unauthorized substitution. The tester shall verify that, for each threat,
the following topics are addressed:
-
Mechanisms used to protect against the threat
-
Which keys are protected by the mechanisms
The mechanisms used may include, but not be limited to, the following:
-
Entry or output of the keys in encrypted form or under split knowledge
procedures (unauthorized disclosure)
-
Use of a cryptographic checksum or some other mechanism that can detect
modifications (unauthorized modification and substitution)
-
Physical controls (unauthorized disclosure, modification, and substitution)
-
Mechanisms that are part of the underlying operating system (unauthorized
disclosure, modification, and substitution)
-
TE08.02.02: The tester shall perform the
following tests:
-
Attempt to access (by circumventing the documented protection mechanisms)
secret and private keys for which the tester is not authorized to have
access. If the module denies access or allows access only to encrypted
or otherwise protected forms of the keys, the requirement is met.
-
Modify all secret and private keys using any method not specified by the
vendor documentation and attempt to load them into the module. The module
should not allow any of the keys to be successfully loaded. The tester
should also attempt to perform cryptographic operations using these keys;
the module should not perform the operations, indicating that the keys
were not loaded.
AS08.03: Public keys shall be protected against
unauthorized modification and substitution. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.03.01: If the module supports public
keys, the vendor documentation shall describe the protection of all public
keys as required by item 1 under VE08.01.01. Protection shall include the
implementation of mechanisms that protect against unauthorized modification
and substitution.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.03.01: If the module supports public
keys, the tester shall verify that the vendor documentation describes how
these keys will be protected from unauthorized modification and unauthorized
substitution. The tester shall verify that, for each threat, the following
topics are addressed:
-
1. Mechanisms used to protect against the threat
-
2. Which keys are protected by the mechanisms
The mechanisms used may include, but not be limited to, the following:
-
Use of a cryptographic checksum or some other mechanism that can detect
modifications (unauthorized modification and substitution)
-
Physical controls (unauthorized modification and substitution)
-
Mechanisms that are part of the underlying operating system (unauthorized
modification and substitution)
-
TE08.03.02: The tester shall modify all public
keys using any method not specified by the vendor documentation and shall
attempt to load them into the module. The module should not allow any of
the keys to be successfully loaded. The tester should also attempt to perform
cryptographic operations using these keys; the module should not perform
the operations, indicating that the keys were not loaded.
Key Generation
AS08.04: A cryptographic module may optionally
implement an internal key generation function. The module shall implement
a FIPS-approved key generation algorithm. Documentation shall specify the
FIPS-approved key generation algorithm that is implemented by the module.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.1 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.04.01: See items 2a and 2b under VE08.01.01
for vendor documentation requirements. They include a description of the
key generation process and the specification of the FIPS-approved key generation
algorithm. The vendor shall also provide proof that the key generation
algorithm is FIPS-approved. This proof shall consist of a validation certificate
from a NIST-accredited laboratory asserting that the algorithm implemented
in the module is a FIPS-approved algorithm. In the absence of a NIST-accredited
laboratory that can validate the algorithm, the vendor organization shall
provide a written affirmation asserting that the algorithm implemented
in the module is a FIPS-approved algorithm.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.04.01: Verification of vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. If the vendor cannot prove that the key
generation algorithm is FIPS-approved or if the algorithm is not documented,
the assertion fails. In addition, the tester shall verify that the implemented
algorithm matches the specified FIPS-approved algorithm and that it is
implemented correctly.
AS08.05: When a random number generator is used
in the key generation process, all values shall be generated randomly or
pseudo-randomly such that all possible combinations of bits and all possible
values are equally likely to be generated. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.5 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.05.01: If the module uses a random number
generator, the vendor documentation of the key generation procedures specified
in item 2 under VE08.02.01 shall also describe how the random number generator
works.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.05.01: If the module uses a random number
generator, the tester shall test the random or pseudo random number generator
using one or more of the statistical and continuous random number generator
tests specified in section 4.11 of FIPS PUB 140-1.
AS08.06: A seed key, if used, shall be entered
in the same manner as cryptographic keys. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.06.01: The key management documentation
shall specify whether a seed key is used for key generation. If so, the
key management documentation shall address entry of the seed key as well
as of other keys.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.06.01: The tester shall review the vendor
documentation to determine whether a seed key is used for key generation.
If so, the tester shall also review the key management documentation and
verify that entry of the seed key is addressed and is identical to the
entry of a cryptographic key.
-
TE08.06.02: The tester shall enter a seed key and
shall verify that the method used to enter it is consistent with the documented
method.
AS08.07: Intermediate key generation states
and values shall not be accessible outside of the module in plaintext or
otherwise unprotected form. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.07.01: Key generation can be considered
as one of the user service states (see AS04.05). Intermediate key generation
states are those states through which the module passes between initiation
and completion of the key generation process. Intermediate key generation
values are interim results from mathematical calculations which eventually
result in a cryptographic key. The finite state machine model (see requirement
4, "Finite State Machine Model") should not include these states and should
not output any intermediate key states or values. The key generation procedures
should not allow any output during the key generation process unless those
values are encrypted.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.07.01: The tester shall review the finite
state machine model and shall verify that no states are defined between
the initiation and the completion of the key generation process. The tester
shall verify that intermediate values are not associated with either the
initiation or completion states of the key generation process. The tester
shall also check the key generation procedures and verify that any specified
outputs are encrypted.
-
TE08.07.02: The tester shall generate a key
and shall attempt to access cryptographic key values during the key generation
process. The module should not display any intermediate values unless they
are encrypted. The tester shall also observe the output interface of the
module and shall verify that any output matches the documented output and
therefore is not a plaintext intermediate value.
Key Distribution
AS08.08: Key distribution may be performed by manual
methods, automated methods, or a combination of automated and manual methods.
A cryptographic module shall implement FIPS-approved key distribution techniques
(e.g., FIPS 171--Key Management Using ANSI X9.17). Until such time as a
FIPS-approved public key-based key distribution technique is established,
commercially available public key methods may be used. Documentation shall
specify the key distribution techniques that are implemented by the module.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.1 , 8.2 , 8.4 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.08.01: See items 3a and 3b under VE08.01.01
for vendor documentation requirements. These include a description of the
key distribution technique and an indication of whether the technique is
FIPS-approved. If the key distribution technique is FIPS-approved, the
vendor shall provide proof in the form of a validation certificate issued
by a NIST-accredited laboratory for the key distribution technique. In
the absence of the certificate, the vendor organization shall provide written
affirmation that the key distribution technique is FIPS-approved. If the
key distribution technique is not FIPS-approved, the vendor documentation
shall explicitly state this.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.08.01: Verification of vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The tester shall determine whether the
key distribution techniques are FIPS-approved; if not, the tester shall
verify from the vendor documentation that a commercial public key-based
key distribution technique is used. In addition, the tester shall verify
that the implemented techniques match the specified FIPS-approved techniques,
and that they are implemented correctly.
Key Entry and Output
AS08.09: Manually distributed cryptographic keys
may be entered into or output from a cryptographic module either by purely
manual methods or by electronic methods. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.09.01: See items 4a through 4f under
VE08.01.01 for vendor documentation requirements.
-
VE08.09.02: In implementing key entry and
output procedures and mechanisms, the vendor shall follow the following
guidelines:
-
If purely manual methods are used for key entry or key output, they may
be one or more of, but not limited to, the following:
-
Keyboard
-
Rotary switches
-
Thumbwheels
-
LCD displays
-
If electronic means are used for key entry or key output, they may be one
or more of, but not limited to, the following:
-
Memory card/token (e.g., magnetic-striped cards, IC chip devices)
-
Smart card/token
-
Electronic key loader
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.09.01: Verification of vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The vendor documentation should provide
the required information on key entry and output procedures and the keys
that are entered into and output by the module; if not, the assertion fails.
-
TE08.09.02: The tester shall enter and output
each of the manually distributed keys and shall verify that they are entered
and/or outputted according to the documentation.
AS08.10: Electronically distributed secret and
private keys shall be entered and output in encrypted form. (1, 2, 3, and
4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.10.01: The vendor documentation shall
specify which types of keys are electronically distributed and the form
in which electronically distributed keys are entered into and output from
the module.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.10.01: If the module supports electronically
distributed keys, the tester shall determine from the vendor documentation
whether secret and private keys are electronically distributed. If so,
the tester shall verify that the vendor documentation specifies that secret
and private keys are entered and output only in encrypted form. If the
documentation specifies that the keys are in any other form, the assertion
fails.
-
TE08.10.02: The tester shall enter every
electronically distributed secret and private key type and shall verify
that the procedure used to enter each key is in accordance with the documented
procedure, including the form that the keys are in when they are entered.
-
TE08.10.03: The tester shall output every
electronically distributed secret and private key type and shall verify
that the procedure used to output each key is in accordance with the documented
procedure, including the form that the keys are in when they are output.
AS08.11: Manually entered cryptographic keys
shall be verified during entry into a cryptographic module for accuracy
using the manual key entry test specified in section 4.11.2. (1, 2, 3,
and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.11.01: See item 4h under VE08.01.01.01
for vendor documentation requirements.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.11.01: Verification of vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The results of the verification should
indicate that the vendor documentation specifies that a manual key entry
test is used to verify all manually entered keys; if not, the assertion
fails.
-
TE08.11.02: The tester shall test the manual
key entry test as documented in AS11.21. If the manual key entry test does
not match the one specified in AS11.21 and if the validation of AS11.21
fails, this assertion fails.
AS08.12: During key entry, keys and key components
may be temporarily displayed to allow visual verification and to improve
accuracy. When encrypted keys or key components are entered, the resulting
plaintext secret or private keys shall not be displayed. (1, 2, 3, and
4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.12.01: The documented key entry procedures
shall allow, if necessary, the display of encrypted keys or key components
during the key entry process, but shall preclude the display of plaintext
secret or private keys that result from the entry of encrypted keys or
key components.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.12.01: The tester shall review the documented
key entry procedures and shall determine whether encrypted keys or key
components can be displayed during the key entry process. If so, the tester
shall verify that the display of plaintext secret or private keys resulting
from the entry of encrypted keys or key components is not allowed during
the key entry process.
-
TE08.12.02: The tester shall enter every
cryptographic key and shall verify that the keys can be temporarily displayed.
When entering encrypted keys or key components, the tester shall also monitor
the output interface of the module to verify that any resulting key material
which is displayed is encrypted.
AS08.13: A means shall be provided to ensure
that a key entered into or output from a module is associated with the
correct entities (i.e., person, group, or process) to which the key is
assigned. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.13.01: The documented key entry/output
procedures shall describe the mechanisms or procedures used to ensure that
each key will be associated with the correct entity.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.13.01: The tester shall review the documented
key entry/output procedures and shall verify that the procedures address
how an entered or output key will be associated with the correct entity.
This association can consist of two components; one resides with the key
and the other resides with the entity. These components are pairwise unique
in that only the combination of a particular entity component with the
correct key component will result in the correct association. These components
can include, but not be limited to:
-
Key component, such as:
-
Keytag
-
Certificate
-
Key encrypted under a hash of the entity component
-
Entity component, such as:
-
Password
-
Personal Identification Number (PIN)
-
Possession of a physical key, token, or equivalent
-
Biometrics (e.g., fingerprint, retina scan, keystroke dynamics)
-
TE08.13.02: For each key that can be entered
or output, the tester shall first output the key while assuming a particular
entity. The tester shall then verify the association between key and entity
by performing one or more of the following tests:
-
The tester shall assume a different entity from the one under which the
key was output. The tester shall then attempt to enter the key and shall
verify that key entry fails.
-
The tester shall, if possible, alter the key component such that the key
is associated with a different entity. The tester shall then assume the
entity under which the key was output, attempt to enter the key, and shall
verify that key entry fails.
AS08.14: For security levels 1 and 2, when manually
distributed secret keys or private keys are entered into or output from
a cryptographic module, they may be entered or output as plaintext keys.
Optionally, the keys may be entered or output either as follows: (1 and
2)
-
In encrypted form
-
Under split knowledge procedures
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.14.01: See item 4g under VE08.01 for
vendor documentation requirement.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.14.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The results of the verification should
indicate that the vendor documentation specifies the form in which all
types of keys are entered and output.
-
TE08.14.02: The tester shall enter every
manually distributed secret and private key and shall verify that the procedure
used to enter each key is in accordance with the documented procedure,
including the form that the keys are in when they are entered.
-
TE08.14.03: The tester shall output every
manually distributed secret and private key and shall verify that the procedure
used to output each key is in accordance with the documented procedure,
including the form that the keys are in when they are output.
AS08.15: For Security Levels 3 and 4, manually
distributed secret keys or private keys shall not be entered into or output
from a cryptographic module in plaintext form. When manually distributed,
secret keys or private keys are entered into or output from a cryptographic
module, they shall be output or entered in either of the following ways:
(3 and 4)
-
In encrypted form
-
Using split knowledge procedures (i.e., as two or more plaintext key
components)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.3 , )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.15.01: See item 4g under VE08.01.01
for vendor documentation requirement.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.15.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The results of the verification should
indicate that the vendor documentation specifies the form in which all
types of keys are entered or output (e.g., encrypted, plaintext, under
split knowledge procedures). The tester shall also check the vendor documentation
to verify that entry or output in plaintext form is not specified for a
secret or private key.
-
TE08.15.02: The tester shall enter every
manually distributed secret and private key and shall verify that the procedure
used to enter each key is in accordance with the documented procedure,
including the form that the keys are in when they are entered.
-
TE08.15.03: The tester shall output every
manually distributed secret and private key and shall verify that the procedure
used to output each key is in accordance with the documented procedure,
including the form that the keys are in when they are output.
AS08.16: When a manually distributed secret
key or private key is entered or output under split knowledge procedures,
the module shall provide the capability to separately authenticate the
operator for each key component. Furthermore, the key components shall
be entered directly into the cryptographic module or output directly from
the cryptographic module (e.g., via a trusted path or directly attached
cable) without traveling through any enclosing or intervening systems where
the components could be stored, combined, or otherwise processed. (3 and
4) A related assertion is AS02.14.
(Relevant Guidance: 8.3 , )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.16.01: If manually distributed secret
or private keys are entered or output under split knowledge procedures,
the vendor documentation shall specify, in the description of the key entry
procedure, that the operator is separately authenticated for each key component.
-
VE08.16.02: The vendor requirement for the
direct entry of the key components is covered under VE02.14.01.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.16.01: If manually distributed, secret
or private keys are entered or output under split knowledge procedures,
the tester shall check the vendor documentation to verify that operator
authentication is specified for each key component.
-
TE08.16.02: In addition to performing the
validation specified by TE08.14.02-03, the tester shall check that authentication
is performed for each key component and that the authentication is in accordance
with the documented key entry and output procedures.
-
TE08.16.03: Validation of the direct entry
of the split knowledge key components was performed under TE02.14.01. If
the tester finds that split key components are not directly entered into
the module, the assertion fails.
Key Storage
AS08.17: When contained within a cryptographic
module, secret and private keys may be stored in plaintext form. These
plaintext keys shall not be accessible from outside the module. This assertion
is related to assertion AS08.02. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.17.01: See items 5a and 5c under VE08.01.01
for vendor documentation requirements.
-
VE08.17.02: The vendor documentation shall
describe the protection of all secret and private keys internal to the
module as specified in VE08.02.01. Protection shall include the implementation
of mechanisms that protect against unauthorized disclosure, modification,
and substitution.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.17.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
specified in VE08.17.01 was performed under TE08.01.01. The results of
the verification should indicate that the vendor documentation specifies
which types of keys are stored and the form in which they are stored (plaintext,
encrypted form, or under split knowledge procedures). Specifically, the
vendor documentation shall indicate whether plaintext secret and private
keys are stored in plaintext form.
-
TE08.17.02: As specified in TE08.02.01 and
TE08.02.02, the tester shall check the vendor documentation to verify that
it includes the specification of protection mechanisms for all secret and
private keys and descriptions of how the mechanisms will protect against
unauthorized disclosure, modification and substitution.
-
TE08.17.03: By using unauthorized means,
the tester shall perform the tests specified in TE08.02.03 that attempt
to access plaintext secret and/or private keys which the documentation
designates as being stored in plaintext form. Note that, at Levels 1 and
2, manually distributed secret and private keys can be output from the
module in plaintext form (see AS08.14). If any of the tests fail, this
assertion fails.
AS08.18: A means shall be provided to ensure
that all keys are associated with the correct entities (i.e., person, group,
or process) to which the keys are assigned. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.18.01: Vendor documentation on key storage
shall describe the mechanisms or procedures used to ensure that each key
will be associated with the correct entity.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.18.01: The tester shall review the documentation
on key storage and shall verify that the procedures address how a stored
key will be associated with the correct entity. This association can consist
of two components; one resides with the key and the other resides with
the entity. These components are pairwise unique in that only the combination
of a particular entity component with the correct key component will result
in the correct association. These components can include, but not be limited
to:
-
Key component, such as:
-
Keytag
-
Certificate
-
Key encrypted under a hash of the entity component
-
Entity component, such as:
-
Password
-
Personal Identification Number (PIN)
-
Possession of a physical key, token, or equivalent
-
Biometrics (e.g., fingerprint, retina scan, keystroke dynamics)
-
TE08.18.02: The tester shall alter the association
of key and entity (e.g., swap keys that belong to two different entities).
The tester shall then attempt to perform cryptographic functions as one
of the entities and shall verify that these functions fail.
Key Destruction
AS08.19: A cryptographic module shall provide the
capability to zeroize all plaintext cryptographic keys and other unprotected
critical security parameters within the module. Zeroization of cryptographic
keys and other critical security parameters is not required if the keys
and parameters are either encrypted or otherwise physically or logically
protected (e.g., contained within an additional embedded FIPS PUB 140-1
cryptographic module. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.19.01: See items 6 under VE08.01.01
for vendor documentation requirements.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.19.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The results of the verification should
indicate that the vendor documentation describes the key destruction mechanism
and specifies any restrictions on when the module can be zeroized, which
keys and security parameters are zeroized, and which keys and security
parameters are not zeroized. In addition, the tester shall verify that
all other keys and parameters that are not zeroized by the zeroize command
are encrypted or are physically or logically protected.
-
TE08.19.02: The tester shall note which keys
are present in the module and initiate the zeroize command. Following the
completion of the zeroize command, the tester shall attempt to perform
cryptographic operations using each of the keys that were stored in the
module and that he or she can access. The tester shall verify that each
key that could be accessed and used had been protected within the module
and that every key that could not be accessed was stored in the module
in plaintext form and was therefore zeroized.
Key Archiving
AS08.20: A cryptographic module optionally may
output keys for archiving purposes. Key outputs for archiving shall be
encrypted. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE08.20.01: If the module supports key archiving,
see items 7a through 7d under VE08.01.01 for vendor documentation requirements.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE08.20.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
was performed under TE08.01.01. The results of the verification should
indicate that the vendor documentation specifies whether key archiving
is used, describes the key archiving technique, and specifies which types
of keys can be archived and whether archived keys are encrypted.
-
TE08.20.02: The tester shall enter each key
that can be archived and shall archive them. The tester shall compare the
archived keys with the plaintext keys and shall verify that the archived
keys are encrypted versions of the plaintext keys.
9. CRYPTOGRAPHIC ALGORITHMS
AS09.01: Cryptographic modules shall employ FIPS-approved
cryptographic algorithms. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.5, 9.1 , 9.2 , 9.3, 9.4 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE09.01.01: The vendor shall provide a NIST
certificate that certifies that the cryptographic module uses FIPS-approved
cryptographic algorithms, and that the implementation of these FIPS-approved
cryptographic algorithms has been tested and passed NIST-approved procedures
and tests at a NIST-accredited facility.
Note: The vendor may also incorporate other (i.e., nonFIPS-approved)
cryptographic algorithms in the cryptographic module.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE09.01.01: The tester shall check to make
sure that the vendor has provided a NIST certificate as described above.
10. ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE/ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY
(EMI/EMC)
AS10.01: Radios shall meet all applicable FCC requirements.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 10.1 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE10.01.01: The vendor shall provide an FCC
certificate certifying that the cryptographic module radio meets all applicable
FCC requirements.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE10.01.01: The tester shall check that the
vendor has supplied the FCC certificate required under VE10.01.01.
AS10.02: A cryptographic module shall conform
to the EMI/EMC requirements specified in FCC Part 15, Subpart J, Class
A (i.e., for business use). (1 and 2)
(Relevant Guidance: 10.1 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE10.02.01: The vendor shall provide an FCC
certificate certifying that the cryptographic module conforms to the EMI/EMC
requirements specified in FCC Part 15, Subpart J, Class A.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE10.02.01: The tester shall check that the
vendor has supplied the FCC certificate required under VE10.02.01.
AS10.03: A cryptographic module shall conform
to the EMI/EMC requirements specified in FCC Part 15, Subpart J, Class
B (i.e., for home use). (3 and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 10.1 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE10.03.01: The vendor shall provide an FCC
certificate certifying that the cryptographic module conforms to the EMI/EMC
requirements specified in FCC Part 15, Subpart J, Class B.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE10.03.01: The tester shall check that the
vendor has supplied the FCC certificate required under VE10.03.01.
11. SELF-TESTS
11.1 General
AS11.01: A cryptographic module shall be able to
perform self-tests in order to ensure that the module is functioning properly.
Certain self-tests shall be performed when the module is powered up (i.e.,
Power-Up Tests) and other self-tests shall be performed under various conditions,
typically when a particular function or operation is performed (i.e., Conditional
Tests). A module may optionally perform other self-tests in addition to
the tests specified in this standard. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 3.1 , )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.01.01: The vendor shall provide a list
of all self-tests, both mandatory and optional, that the module can perform.
This list shall include both power-up tests and conditional tests.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.01.01: The tester shall inspect the
list of self-tests to verify that it includes the following:
-
Power-up tests
-
Cryptographic algorithm test
-
Software/firmware test
-
Critical functions test
-
Statistical random number generator tests (required at Levels 3 and 4)
-
Other self-tests which are performed at power-up and on demand
-
Conditional tests
-
Pairwise consistency test (if the module generates public and private keys)
-
Software/firmware load test
-
Manual key entry test
-
Statistical random number generator test
-
Other conditional tests
All of the power-up and conditional self-tests are defined in section 4.11
of the FIPS and will be explicitly defined later in the appropriate assertions.
-
TE11.01.02: Specific validation requirements
for these self-tests are specified under AS11.05 through AS11.22. Note
that, in general, power-up self-tests cannot be verified by actual testing
because they involve internals of the module to which the tester would
not have access, such as the cryptographic algorithm. Causing the module
to fail a particular self-test in order to verify that the correct failure
indicator is output, for example, would be an appropriate test, but the
module generally would not have a mechanism that would allow the tester
to force it to fail. Therefore, the tester may have to resort to code and/or
design review.
AS11.02: Whenever a cryptographic module fails
a self-test, the module shall enter an error state and output an error
indicator via the status interface. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.02.01: The vendor shall document all
error states associated with each self-test and shall indicate for each
error state the expected error indicator.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.02.01: The tester shall inspect the
vendor documentation, check that it lists every error state that the module
enters upon failure of a self-test, and indicates the error indicator associated
with each error state. The tester shall compare the list of error states
to those defined in the finite state machine model (see AS04.01) to verify
that they agree.
-
TE11.02.02: By inspecting the code and/or
design documentation that specifies how each self-test handles errors,
the tester shall verify that:
-
The module enters an error state upon failing a self-test.
-
The error state is consistent with the documentation and the finite state
machine model.
-
The module outputs an error indicator.
-
The error indicator is consistent with the documented error indicator.
-
TE11.02.03: If the module design and operating
procedures allow it, the tester shall run self-tests and cause the module
to enter every error state. The tester shall compare the observed error
indicator with the indicator specified in the vendor documentation. If
they are not the same, the assertion is failed.
AS11.03: The module shall not perform any cryptographic
functions while in the error state and no data shall be output via the
data output interface while the error condition exists. Related assertions
are AS02.04 and AS04.07. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.03.01: See VE02.04.01 for the vendor
design requirement. Also, the vendor design shall ensure that cryptographic
operations cannot be performed while the module is in the error state.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.03.01: Tester verification of the inhibition
of output was performed under TE02.04.01, TE02.04.02, and TE04.07.01. The
results of the verification should indicate that:
-
The vendor documentation shows that all data output via the data output
interface is inhibited whenever the module is in an error state.
-
If testable, the module inhibits all data output when the module is in
an error state.
-
TE11.03.02: The tester shall check that vendor
documentation indicates cryptographic functions are inhibited while the
module is in an error state. Cryptographic functions include the following:
-
Encryption
-
Decryption
-
Secure message hashing
-
Digital signature creation and verification
-
Other operations that require the use of cryptography
-
TE11.03.03: If the module design and operating
procedures allow it, the tester shall put the module in an error state
and verify that any cryptographic operations that the tester attempts to
initiate are prevented.
AS11.04: Each possible error condition shall
be documented along with the actions necessary to clear the error and resume
normal operation (possibly including maintenance, servicing or repair of
the module). (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.04.01: The vendor documentation shall
provide for each error condition, its name, the events that can produce
it, and the actions necessary to clear it and resume normal operation.
Note that necessary action may include sending the module to the manufacturer
for repair.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.04.01: The tester shall check that the
information provided above is specified for each error condition.
-
TE11.04.02: If the module design and operating
procedures allow it, the tester shall cause each error condition to occur
and shall attempt to clear the error condition. The tester shall verify
that actions necessary to clear the error condition are consistent with
the vendor documentation. If the tester cannot cause each error condition
to occur, the tester shall review the code listing and or design documentation
to determine whether the actions necessary to clear each error condition
are consistent with the descriptions in the vendor documentation.
11.2. Power-Up Tests
General
AS11.05: After a cryptographic module is powered
up, the module shall enter the self-test state and perform at least the
following tests: cryptographic algorithm test, software/firmware test,
critical functions test and statistical random number generator tests.
The module may optionally perform additional tests. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.05.01: See VE11.01.01 for the vendor
requirement. Note that the running of statistical random number generator
tests at power up is required for Level 4 and optional for the other levels.
Also, the vendor shall document any optional power-up self-tests.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.05.01: Verification of the documented
list of power-up self-tests was performed under TE11.01. Verification that
the module performs the self-tests as documented is done under validation
requirements for AS11.10-AS11.18.
-
TE11.05.02: If the module design and operating
procedures allow it, the tester shall perform all optional power-up self-tests
and shall verify that they perform as documented. If the tester cannot
perform tests on the self-tests to validate them, the tester shall review
the code listing and/or design documentation to determine whether the optional
self-tests have been implemented as documented. If the module has the capability
of displaying which self-tests are running, the tester shall run the optional
self-tests to verify that the module performs them.
AS11.06: The power-up tests shall not require
operator intervention in order to run. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.06.01: The vendor documentation shall
require that the running of power-up self-tests not involve any inputs
from or actions by the operator.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.06.01: To test that, upon power-up,
the module performs the power-up self-tests without requiring any operator
intervention, the tester shall power-up the module. If the tester must
enter any inputs or perform any actions while the self-tests are running,
the assertion fails.
-
TE11.06.02: To test that, upon command from
an operator, the module performs the power-up self-tests without requiring
any operator intervention, the tester shall command the module to perform
the self-tests. If the tester must enter any inputs or perform any actions
while the self-tests are running, the assertion fails.
AS11.07: If all of the power-up tests are passed
successfully, such an indication shall be output via the "status output"
interface. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.07.01: The vendor shall document the
indicator that the module outputs upon successful completion of all of
the power-up self-tests.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.07.01: The tester shall check the vendor
documentation and shall verify that it specifies an indicator that is output
from the status output interface upon successful completion of all of the
power-up self-tests.
-
TE11.07.02: To test the assertion, the tester
shall power-up the module and shall monitor the status output interface.
The expected indicator from the status output interface should be consistent
with the documented indicator.
-
TE11.07.03: To test the assertion, the tester
shall command the module to perform the self-tests and shall monitor the
status output interface. The expected indicator from the status output
interface should be consistent with the documented indicator.
AS11.08: All data output shall be inhibited
when these tests are performed. A related assertion is AS02.04. (1, 2,
3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.08.01: See VE02.04.02 for the vendor
documentation requirement.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.08.01: Tester verification of the inhibition
of output during self-tests was performed under TE02.04.03 and TE02.04.04.
The results of the verification should indicate that:
-
The vendor documentation shows that all data output is inhibited when the
module is in a self-test condition.
-
If testable, the module inhibits all data output when running a self-test.
AS11.09: The module shall provide a means to
initiate the tests on demand for periodic testing of the module. (1, 2,
3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 11.1 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.09.01: The vendor shall describe the
procedure by which an operator can initiate the power-up self-tests on
demand. All of the power-up self-tests must be included. Note that operator
initiation of the statistical random number generator tests are optional
for Levels 1 and 2.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.09.01: The tester shall inspect the
vendor documentation to verify that initiation of self-tests on demand
is specified for all of the power-up self-tests. Note that, for Levels
1 and 2, operator initiation of statistical random number generator tests
is optional. The documentation shall also include what steps an operator
must take in order to initiate the self-tests.
-
TE11.09.02: To test that the necessary steps
to initiate the self-tests (e.g., the actual command that the operator
must send to the module) are consistent with that specified in the vendor
documentation, the tester shall command the module to perform the power-up
self-tests. If the steps that the tester performs are not consistent with
those in the documentation, the assertion is failed.
Cryptographic algorithm test
AS11.10: The cryptographic algorithms shall be
tested by operating the algorithm on data for which the correct output
is already known (i.e., a "known answer" test). The test is passed if the
calculated output equals the previously generated output. (1, 2, 3, and
4)
(Relevant Guidance: 11.2 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.10.01: The vendor shall document the
known answer test that should be performed for the cryptographic algorithm
test.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.10.01: The tester shall inspect the
vendor documentation to determine whether it includes the following steps
for the cryptographic algorithm test:
-
Use of a known answer
-
Calculations that should equal the known answer
-
Comparison of the calculated answer against the known answer
-
Successful indication if calculated equals known, otherwise failure
-
TE11.10.02: By reviewing the code listing
and/or design documentation and comparing it with the vendor documentation,
the tester shall verify that the implementation of the known answer test
is consistent with the vendor documentation.
AS11.11: A known answer test shall be run for
each cryptographic function (e.g., encryption, decryption, authentication)
that is implemented. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 11.2 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.11.01: In the vendor documentation of
the known answer test, the vendor shall indicate that all of the cryptographic
functions are tested by the known answer test and shall list them.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.11.01: By checking the vendor documentation,
the tester shall verify that a known answer test is associated with each
cryptographic function. The list of cryptographic functions shall include
the following:
-
Encryption
-
Decryption
-
Secure message hashing
-
Digital signature creation and verification
-
Other operations that require the use of cryptography
-
TE11.11.02: By analyzing the code listing
and/or design documentation, the tester shall verify that the implementation
of the cryptographic algorithm test includes the initiation of known answer
tests for all of the cryptographic functions.
AS11.12: Message digest algorithms shall either
have an independent known answer test or shall be included in the known
answer test of the cryptographic algorithm in which they are included.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.12.01: If the module implements message
digest algorithms, the vendor shall specify which known answer test is
used to test it.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.12.01: The tester shall determine whether
the module implements a message digest algorithm. If so, the tester shall
verify that the vendor documentation specifies whether the message digest
algorithm has its own known answer test or whether it is included in the
known answer test of another algorithm.
-
TE11.12.02: By checking the code listing
and/or design documentation, the tester shall verify that the module uses
either a separate known answer test or the known answer test of an algorithm
in order to test a message digest algorithm.
AS11.13: A cryptographic module may omit the
cryptographic algorithm test if the module includes two independent cryptographic
algorithm implementations whose output are continually compared in order
to ensure the correct functioning of the cryptographic algorithm. Whenever
the output of the two implementations are not equal, the module shall enter
an error state and output an error indicator via the status interface.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.13.01: The vendor shall specify whether
a known answer test or the comparison of the output of two independent
cryptographic algorithm implementations (compared answer test) is used
to test the module's cryptographic algorithm. If the compared answer test
is used, the vendor shall document it.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.13.01: The tester shall determine from
the vendor documentation whether a known answer test or a compared answer
test is used to test the module's cryptographic algorithm. If the compared
answer test is used, the tester shall determine whether the documentation
of the compared answer test includes:
-
Use of two independent cryptographic algorithm implementations
-
Continual comparison of the outputs of the algorithm implementation
-
Transition into an error state and output of an error indicator when the
two outputs are not equal
-
TE11.13.02: By checking the code and/or design
documentation, the tester shall verify that the module implements the documented
steps for performing a compared answer test.
-
TE11.13.03: Validation of whether the module
enters the error state and outputs an error indicator upon failure of the
self-test is performed under TE11.02.01, TE11.02.02, and TE11.02.03. If
any of these tests fail, this assertion fails.
Software/firmware test
AS11.14: An error detection code (EDC) or FIPS-approved
authentication technique (e.g. the computation and verification of a data
authentication code or NIST digital signature algorithm) shall be calculated
on and stored with all software and firmware residing in the module (e.g.,
within EEPROM and RAM). This error detection code, data authentication
code, or digital signature shall then be verified when the power-up self-tests
are run. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 7.1 , 11.4, 11.5 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.14.01: The vendor documentation shall
specify whether an error detection code (EDC) or a FIPS-approved authentication
technique (e.g., FIPS-approved data authentication code (DAC) or NIST digital
signature) will be used to provide integrity for all resident software
and firmware. If the module implements a FIPS-approved authentication technique,
the vendor shall provide proof that shall consist of a validation certificate
from a NIST-approved laboratory asserting that the authentication technique
implemented in the module is FIPS-approved. In the absence of such a validation
certificate, the vendor organization shall provide a written affirmation
asserting that the authentication technique implemented in the module is
FIPS-approved. The documentation shall describe the implemented integrity
mechanism.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.14.01: The tester shall determine from
the proof provided by the vendor whether the authentication technique implemented
in the module is FIPS-approved. If the tester cannot determine this, the
assertion fails.
-
TE11.14.02: If the module implements EDCs
for software/firmware integrity, the tester shall verify that the vendor
documentation of the software/firmware test includes:
-
Description of EDC algorithm.
-
Identification of software and firmware that is protected using EDCs.
-
Calculation of the EDCs when the software and firmware is installed
-
Recalculation of the EDCs when the self-test is initiated
-
Comparison of the stored EDC against the recalculated EDC
-
Failure of the self-test when the two EDCs are not equal
-
TE11.14.03: If the module implements a DAC
for software/firmware integrity, the tester shall verify that the vendor
documentation of the software/firmware test fully describes the process
bywhich the DAC is calculated and verified. The following example is the
DES cipher-block chaining method for calculating DACs:
-
Divide software into 64-bit blocks
-
Compute the XOR of the first block and an initialization vector
-
Encrypt the result
-
XOR the encrypted result with the next block and encrypt
-
Repeat the XOR and encryption until the last block has been processed.
The last block to be processed is the DAC.
-
TE11.14.04: If the module implements the
NIST digital signature for software/firmware integrity, the tester shall
verify that the vendor documentation of the software/firmware test includes
the following:
-
Description of digital signature algorithm
-
Identification of software and firmware that is protected using digital
signatures.
-
Calculation of digital signatures when the software and firmware is installed
-
Verification of the digital signature when the self-test is initiated
-
Failure of the self-test upon failure of the digital signature verification
-
TE11.14.05: By checking the code and/or design
documentation, the tester shall verify that the implementation of the software/firmware
test is consistent with either TE11.14.01, TE11.14.02, or TE11.14.03.
-
TE11.14.06: If possible, the tester shall
test the module by modifying the stored software, firmware, or the implemented
integrity mechanism and initiating the self-tests, and observing the output
from the status output interface. If no indicator is output which indicates
that the software/firmware self-test failed, the assertion fails.
Critical functions test
AS11.15: All other functions that are critical
to the secure operation of the module and can be tested as part of the
power-up tests shall be tested. Documentation shall provide a complete
specification of all critical functions and the nature of the power-up
self-tests designed to test those functions. Other critical functions that
are performed under certain specific conditions are tested as part of the
conditional tests. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.15.01: Critical functions can be defined
as those functions that could lead to the disclosure of plaintext information,
including data and cryptographic keys, if they fail. Examples of critical
functions include random/pseudo-random number generation, operation of
the cryptographic algorithm, and cryptographic bypass.
-
VE11.15.02: The vendor shall provide a matrix
of all critical functions. For each critical function, the vendor shall
indicate:
-
Its purpose (e.g., why is it a "critical" function
-
Which critical functions are tested by which power-up tests
-
Which critical functions are tested by which conditional tests
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.15.01: The tester shall review the vendor-supplied
matrix that identifies the critical functions and the self-tests that are
designed to test them. This documentation shall include the following:
-
Identification and description of all critical functions
-
Identification of at least one self-test for every critical function
The critical functions must include, but not be limited to, random number
generation and operation of the cryptographic algorithm. Optional critical
functions, such as pseudo-random number generation and cryptographic bypass,
must have critical functions tests only if they are implemented in the
module.
-
TE11.15.02: By checking the code and/or design
documentation, the tester shall verify that the module performs the specified
self-tests for each critical function.
Statistical Random Number Generator Tests
AS11.16: Cryptographic modules that implement a
random or pseudorandom number generator shall incorporate the capability
to perform statistical tests for randomness. The four tests specified in
FIPS PUB140-1 are recommended. However, alternative tests which provide
equivalent or superior randomness checking may be substituted. If any of
the tests fail, the module shall enter an error state. A related assertion
is AS11.02. (3 and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.5 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.16.01: If the module implements a random
or pseudorandom number generator, the vendor documentation shall specify
statistical tests for randomness. These tests are optional at Levels 1
and 2. The randomness tests implemented by the module can consist of, but
are not limited to, all of the following tests that are recommended by
section 4.11.1 of FIPS PUB 140-1:
-
Monobit Test
-
Poker Test
-
Runs Test
-
Long Run Test
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.16.01: If the module implements a random
or pseudorandom number generator, the tester shall check the vendor documentation
to verify that statistical tests for randomness are specified if the module
is meant to meet either Level 3 or Level 4; if the module is a Level 1
or 2 module, the statistical random number generator tests are optional.
-
TE11.16.02: The tester shall determine from
the vendor documentation whether the statistical tests recommended in section
4.11.1 of FIPS PUB 140-1 are implemented by the module. If so, the tester
shall review the specification of the statistical tests in the code and/or
design documentation to determine whether they have been implemented as
specified in FIPS PUB 140-1 and that the module enters an error state if
any of them fail. The specifications of the recommended tests are based
on a single bit stream of 20,000 consecutive bits of output and are as
follows:
-
Monobit Test
-
Count the number of ones in the 20,000 bit stream. Denote this quantity
by X.
-
The test is passed if 9,654 < X < 10,346
-
Poker Test
-
Divide the 20,000 bit stream into 5,000 contiguous 4-bit segments. Count
and store the number of occurrences of each of the 16 possible 4-bit values.
Denote f(i) as the number of each 4-bit value i where 0 <=
i <= 15
-
Evaluate the following:
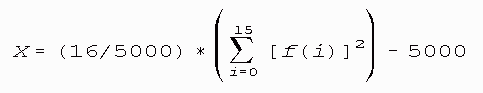
-
The test is passed if 1.03 < X < 57.4
-
Runs Test
-
A run is defined as a maximal sequence of consecutive bits of either all
ones or all zeros, which is part of the 20,000 bit sample stream. The incidences
of runs (for both consecutive zeros and consecutive ones) of all lengths
(>= 1) in the sample stream should be counted and stored.
-
The test is passed if the number of runs that occurs (of length 1 through
6) is each within the corresponding interval specified below. This must
hold for both the zeros and ones; that is, all 12 counts must lie in the
specified interval. For the purpose of this test, runs of greater than
6 are considered to be of length 6.
| Length of Run |
Required Interval |
| 1 |
2,267-2733 |
| 2 |
1,079-1,421 |
| 3 |
502-748 |
| 4 |
223-402 |
| 5 |
90-223 |
| 6 + |
90-223 |
-
Long Run Test
-
A long run is defined to be a run of length 34 or more (of either zeros
or ones).
-
On the sample of 20,000 bits, the test is passed if there are NO long runs.
-
TE11.16.03: If the module implements statistical
tests other than those recommended in FIPS PUB 140-1, the tester shall
determine from the vendor documentation whether they provide equivalent
or superior randomness checking. If not, this assertion fails.
AS11.17: For Level 3, the statistical tests
shall be callable upon demand. A related assertion is AS11.09. (3)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.17.01: See VE11.09.01 for the vendor
documentation requirement for tests that can be initiated by the operator.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.17.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
and the ability to initiate the tests upon demand was performed under TE11.09.01-02.
If the statistical tests cannot be initiated from at least one authorized
role upon demand, this assertion fails.
AS11.18: For Level 4, the statistical tests
shall be performed at power-up and shall also be callable upon demand.
Related assertions are AS11.05 and AS11.09. (4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.18.01: See VE11.05.01 for the vendor
requirement that statistical tests be performed at power-up. See VE11.09.01
for the vendor requirement that these tests be callable upon demand by
an operator.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.18.01: Verification of the vendor documentation
was performed under TE11.05.01 and TE11.09.01. Verification that the tests
are performed at power-up was performed under TE11.05.02. Verification
that the tests can be initiated on demand by an operator was performed
under TE11.09.02. If either of the verifications fail, this assertion fails.
11.3 Conditional Tests
Pairwise consistency test
AS11.19: Cryptographic modules that generate public
and private keys shall test the keys for pairwise consistency. If the keys
are to be used only for the calculation and verification of digital signatures,
then the consistency of the keys shall be tested by the calculation and
verification of a signature. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 11.2 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.19.01: If the module generates public
and private keys, the vendor documentation shall describe how the keys
are used by the module. If the keys are used for encryption/decryption,
the documentation shall describe a pairwise consistency test that is based
on encryption/decryption. If the keys are used for the calculation and
verification of digital signatures, either in addition to or in lieu of
being used for encryption/decryption, the documentation shall describe
a pairwise consistency test which is based on the calculation and verification
of a digital signature.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.19.01: The tester shall determine from
the vendor documentation whether the module generates public and private
keys. If so, the tester shall check that the documentation describes one
or more pairwise consistency tests based on how the keys are used by the
module (encryption/decryption, digital signatures, or both).
-
TE11.19.02: If public and private keys are
used for encryption/decryption, the tester shall verify that the implementation
of the pairwise consistency check is consistent with the vendor documentation
by checking the code and/or design documentation. In performing the verification,
the tester shall consider the following example of a pairwise consistency
test for keys that are used to perform inverse functions:
-
Apply the public key to a plaintext value.
-
Compare the result to the original plaintext; if they are the same, the
test is failed.
-
Apply the private key to the ciphertext value.
-
Compare the result to the plaintext value; if they are not the same, the
test is failed.
-
TE11.19.03: If public and private keys are
used for the calculation and verification of digital signatures, the tester
shall verify the implementation of the pairwise consistency check is consistent
with the vendor documentation by checking the code and/or design documentation.
In performing the verification, the tester shall consider the following
example, based on the NIST Digital Signature Standard (DSS), of a pairwise
consistency test for keys that are used to calculate and verify digital
signatures:
-
Apply a secure hash algorithm to a message to create a message digest
-
Input the message digest and the private key into a digital signature algorithm
to create the signature
-
Input the message digest, the public key, and the signature into the verification
algorithm
-
The assertion is satisfied only if the verification succeeds
Software/firmware load test
AS11.20: A cryptographic mechanism using a FIPS-approved
authentication technique (e.g., a data authentication code or NIST digital
signature algorithm) shall be applied to all validated software and firmware
that can be externally loaded into a cryptographic module. This test shall
verify the data authentication code or digital signature whenever the software
or firmware is externally loaded into the module. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 11.3, 11.5 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.20.01: The vendor documentation shall
describe the FIPS-approved authentication technique used to protect the
integrity of all externally loaded software and firmware. The vendor shall
provide proof that the technique is FIPS-approved. This proof shall consist
of a validation certificate from a NIST-approved laboratory asserting that
the authentication technique implemented in the module is FIPS-approved.
In the absence of the validation certificate, the vendor organization shall
provide a written affirmation asserting that the authentication technique
implemented in the module is FIPS-approved.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.20.01: The tester shall determine from
the proof provided by the vendor whether the authentication technique implemented
in the module is FIPS-approved. If the tester cannot determine this, the
assertion fails.
-
TE11.20.02: If the module implements a DAC,
the tester shall check the vendor documentation, code, and/or design documentation
to verify that the software/firmware load test in the module fully implements
the process by which the DAC is calculated and verified. The following
example is the DES cipher-block chaining method for calculating DACs:
-
Divide software into 64-bit blocks
-
Compute the XOR of the first block and an initialization vector
-
Encrypt the result
-
XOR the encrypted result with the next block and encrypt
-
Repeat the XOR and encryption until the last block has been processed.
The last block to be processed is the DAC.
-
TE11.20.03: If the module implements the
NIST digital signature for software/firmware integrity, the tester shall
check the vendor documentation, code, and/or design documentation to verify
that the software/firmware load test implemented in the module includes
the following:
-
Description of digital signature algorithm
-
Identification of software and firmware that is protected using digital
signatures.
-
Calculation of digital signatures when the software and firmware is installed
-
Verification of the digital signature when the self-test is initiated
-
Failure of the self-test upon failure of the digital signature verification
-
TE11.20.04: The tester shall modify the software,
firmware, DAC, or digital signature associated with software/firmware that
must be loaded, load the software/firmware, and verify that the module
fails the self-test.
Manual key entry test
AS11.21: When cryptographic keys or key components
are manually entered into a cryptographic module, the keys shall have an
error detection code (e.g., a parity check value) or shall use duplicate
entries in order to verify the accuracy of the entered keys. A cryptographic
module shall verify the error detection code or duplicate entries and provide
an indication of the success or failure of the entry process. (1, 2, 3,
and 4)
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.21.01: The vendor shall document the
manual key entry test. Depending on whether error detection codes or duplicate
key entries are used, the manual key entry test shall include the following:
-
Error detection codes (EDCs):
-
Description of EDC calculation algorithm
-
Description of verification process
-
Expected outputs for success or failure of test
-
Duplicate key entries:
-
Description of verification process
-
Expected outputs for success or failure of test
-
VE11.21.02: If EDCs are associated with keys,
then the vendor documentation that describes the format of the cryptographic
keys (see AS08.01) shall include fields for the error detection codes.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.21.01: The tester shall determine from
the vendor documentation which method is used for the manual key entry
test (error detection codes or duplicate key entries). Based on the method
used, the tester shall check the vendor documentation, code, and/or design
documentation that addresses the implementation of the manual key entry
test to determine whether the following information is included:
-
Error detection codes:
-
Key format for all manually-entered keys, including fields for EDCs (see
AS08.01)
-
Description of EDC algorithm
-
Description of EDC verification process
-
All expected outputs for success or failure of the test
-
Duplicate key entries:
-
Duplicate key entries for all manually-entered keys
-
Description of duplicate key, entry verification process
-
All expected outputs for success or failure of the test
-
TE11.21.02: For manual key entry tests using
EDCs, the tester shall perform the following tests:
-
The tester shall enter each type of manually-entered key without any errors
and shall observe the status output interface. If no indicator is detected,
or if the indicator does not match the documented indicator for the success
of the manual key entry test, the test is failed.
-
The tester shall attempt to perform cryptographic operations with each
entered key to verify that it was entered correctly.
-
The tester shall change either the EDC associated with each manually-entered
key or the key itself and shall enter them into the module. The tester
shall observe the indicator that is output from the status output interface;
if no output is detected, or the indicator does not match the documented
indicator for the failure of the manual key entry test, the test is failed.
-
The tester shall attempt to perform cryptographic operations with each
key that was not successfully entered. Each operation using each key should
fail, verifying that the key was not entered.
-
TE11.21.03: For manual key entry tests using
duplicate key entries, the tester shall perform the following tests:
-
The tester shall enter each type of manually-entered key without any errors
and shall observe the status output interface. If no indicator is detected,
or if the indicator does not match the documented indicator for the success
of the manual key entry test, the test is failed.
-
The tester shall attempt to perform cryptographic operations with each
entered key to verify that it was entered correctly.
-
The tester shall alter the accuracy of one of the manually entered keys,
either the first or second duplicate entry, and shall enter them into the
module. The tester shall observe the indicator that is output from the
status output interface; if no output is detected, or the indicator does
not match the documented indicator for the failure of the manual key entry
test, the test is failed.
-
The tester shall attempt to perform cryptographic operations with each
key that was not successfully entered. Each operation using each key should
fail, verifying that the key was not entered.
Continuous Random Number Generator Test
AS11.22: Cryptographic modules that implement a
random or pseudorandom number generator shall test the generator for failure
to a constant value. If the generator produces blocks of n bits, where
n > 15, the first block generated after power-up shall not be used, but
shall be saved for comparison with the next block to be generated. Upon
each subsequent generation, the newly generated block is compared with
the previously generated block. The test fails if the two compared blocks
are equal. If each call to the generator produces fewer than 16 bits, then
the first n bits generated after power-up, for some n > 15, shall not be
used, but shall be saved for comparison with the next n generated bits.
Each subsequent generation of n bits shall be compared with the previously
generated n bits. The test fails if two compared n-bit sequences are equal.
(1, 2, 3, and 4)
(Relevant Guidance: 8.5 )
Required Vendor Information
-
VE11.22.01: If the module implements a random
or pseudorandom number generator, the vendor shall document the continuous
random number generator test.
Required Test Procedures
-
TE11.22.01: The tester shall determine whether
the module implements a random or pseudorandom number generator. If so,
the tester shall check the documentation, code and/or design documentation
that addresses of the continuous random number generator test to verify
that it implements the specifics of the test. If the generator generates
blocks of n bits, where n > 15, then the tester shall verify that the implementation
of the test includes:
-
Storage of first block for comparison against the next block
-
Comparison of each subsequently generated block against the previously
generated block
-
Failure of the test if two compared blocks are equal
If the generator consistently generates fewer than 16 bits, then the tester
shall verify that the implementation of the test includes the following:
-
Storage of the first n bits, where n > 15, for comparison against the next
n generated bits
-
Comparison of each subsequently generated n bits against the previously
generated n bits
-
Failure of the test if two compared n-bit sequences are equal
Continue to Appendix A: A Cryptographic Module Security Policy
Need assistance?
Last Update: January 10, 2002
Computer Security Division
National Institute of Standards and Technology