Combinatorial methods can reduce costs for software testing, and have significant applications in software engineering:
- Combinatorial or t-way testing is a proven method for more effective testing at lower cost.
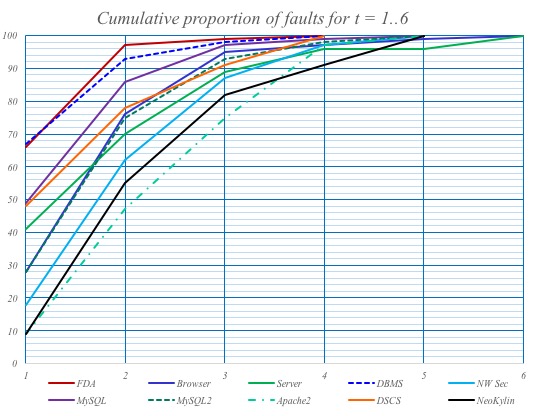 The key insight underlying its effectiveness resulted from a series of studies by NIST from 1999 to 2004. NIST research showed that most software bugs and failures are caused by one or two parameters, with progressively fewer by three or more, which means that combinatorial testing can provide more efficient fault detection than conventional methods. Multiple studies have shown fault detection equal to exhaustive testing with a 20X to 700X reduction in test set size. New algorithms compressing combinations into a small number of tests have made this method practical for industrial use, providing better testing at lower cost. See articles on high assurance software testing or security and reliability.
The key insight underlying its effectiveness resulted from a series of studies by NIST from 1999 to 2004. NIST research showed that most software bugs and failures are caused by one or two parameters, with progressively fewer by three or more, which means that combinatorial testing can provide more efficient fault detection than conventional methods. Multiple studies have shown fault detection equal to exhaustive testing with a 20X to 700X reduction in test set size. New algorithms compressing combinations into a small number of tests have made this method practical for industrial use, providing better testing at lower cost. See articles on high assurance software testing or security and reliability.
- Autonomous systems assurance: Input space coverage measurements are needed in life-critical assurance and verification of autonomous systems, because current methods for assurance of safety critical systems rely on measures of structural coverage, which do not apply to many autonomous systems. Combinatorial methods, including a theorem relating measures of input space coverage, offer a better approach for autonomous system verification.
- Metrology* for software engineering. Sound engineering requires adequate measurement and analysis. Structural coverage enables formally defined criteria for test completeness, but even full coverage may miss faults related to rare inputs. Combinatorial methods open new possibilities for metrology in software engineering, providing a more scientific approach to assurance and verification.
*Metrology is the science of measurement (NIST is the US national metrology institute).
NEW: Combinatorial Coverage Difference Measurement for assurance of autonomous systems and other critical software.
Examples and Case Studies - from some of the world's largest organizations, including Adobe, Avaya, Bosch, IBM, Jaguar Land Rover, Lockheed Martin, Mercedez Benz, US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Red Hat, Rockwell Collins, Siemens, the US Air Force, US Army, US Marine Corps, US Navy, and others.
- Industrial examples - - Autonomous systems - - Cybersecurity -
FREELY AVAILABLE SOFTWARE More than 4,000 corporate and university users
> Version 3.2 of ACTS released Sept. 30, 2019 <
Software on this site is free of charge and will remain free in the future. It is public domain; no license is required and there are no restrictions on use. You are free to include it and redistribute it in commercial products if desired. NIST is a US Government agency, doing research in advanced measurement and test methods.
To obtain the tools, please send a request to Rick Kuhn - kuhn@nist.gov. Please provide first and last name, and organization. We will send you a download link.
QUICK START - It's easy to learn the basics of this method!
ORACLE-FREE TESTING
Combinatorial methods make it possible to detect a significant number of faults without a conventional test oracle. This seemingly impossible task is achieved using two layers of covering arrays with equivalence classes. A U.S. patent (#10552300) has been issued for this method, but this patent does not apply to ACTS or any other tools on this site; these tools are public domain. For more information on the oracle-free testing method, please contact our Technology Partnerships Office.
SOME OF OUR ACCOMPLISHMENTS TO DATE INCLUDE:
- Empirical finding that software failures are triggered by interactions of only a few variables (1 to 6)
- IPOG covering array algorithm and its variants, more efficient than other known algorithms
- Developed sequence covering arrays, extending combinatorial methods to event sequence testing
- Measurement science and tools for combinatorial coverage
- Theorem relating (static) combinatorial input space coverage to (dynamic) structural code coverage, and
- Methods for error detection without conventional test oracle
Contacts: Rick Kuhn or Raghu Kacker kuhn@nist.gov, raghu.kacker@nist.gov
Disclaimer: Software products are identified in this document. Such identification does not imply recommendation by NIST, or that the products identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
 An unofficial archive of your favorite United States government website
An unofficial archive of your favorite United States government website


